Passive Assets
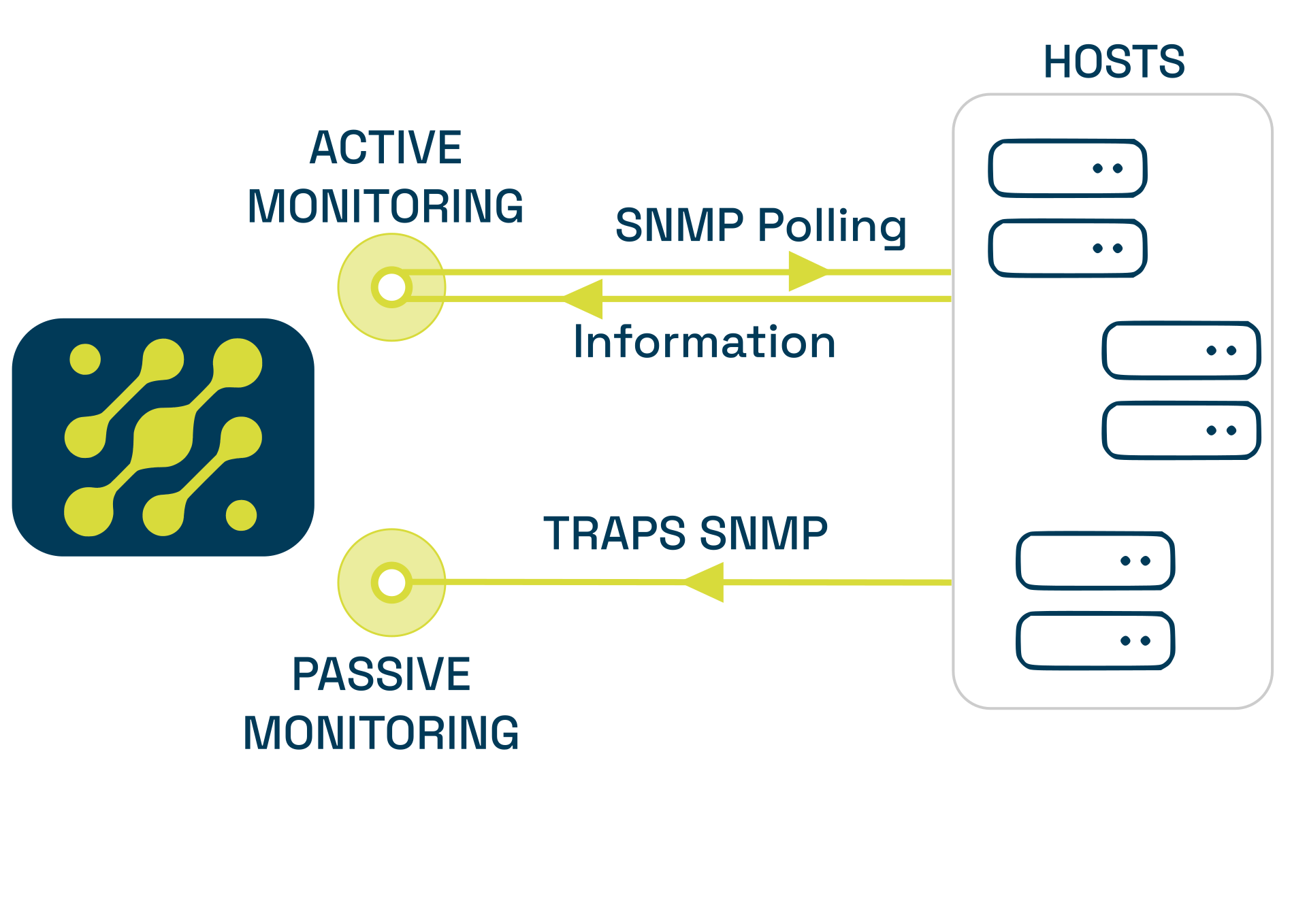
Within network monitoring, two important methods are distinguished: Active Monitoring and Passive Monitoring. Broadly speaking, while active monitoring is regular in terms of requests for operational status (regardless of whether or not a change has occurred), passive monitoring is asynchronous, i.e. it receives only the events related to these changes, which is a very efficient way of monitoring, as it consumes very few resources.
These monitoring methodologies are different, but equally useful. However, WOCU-Monitoring is able to integrate the combined use of them, taking advantage of the benefits they present.
The system has an event indexing backend that is used to receive and store events from the passive monitoring world, such as with SNMP Traps.
From the Passive Assets section the user is able to import, model and configure new passive monitoring services and bind them to network devices to fulfil their communication function from the passive approach and without the involvement of any Monitoring Pack.
Passive Services
First instance of the Passive Monitoring alternative method configuration ecosystem.
From this location the user can link Passive Services Passive Services, previously created from the section Passive Services Templates, to one or more monitored Hosts. It is also possible to permanently unlink such correlations.
Note
A Template on its own has no value in the system, it must be linked to a Host in order to originate a functionally operational Passive Service.
Therefore, the Passive Services table hosts the links between Hosts and Passive Services registered and already operational in WOCU-Monitoring.
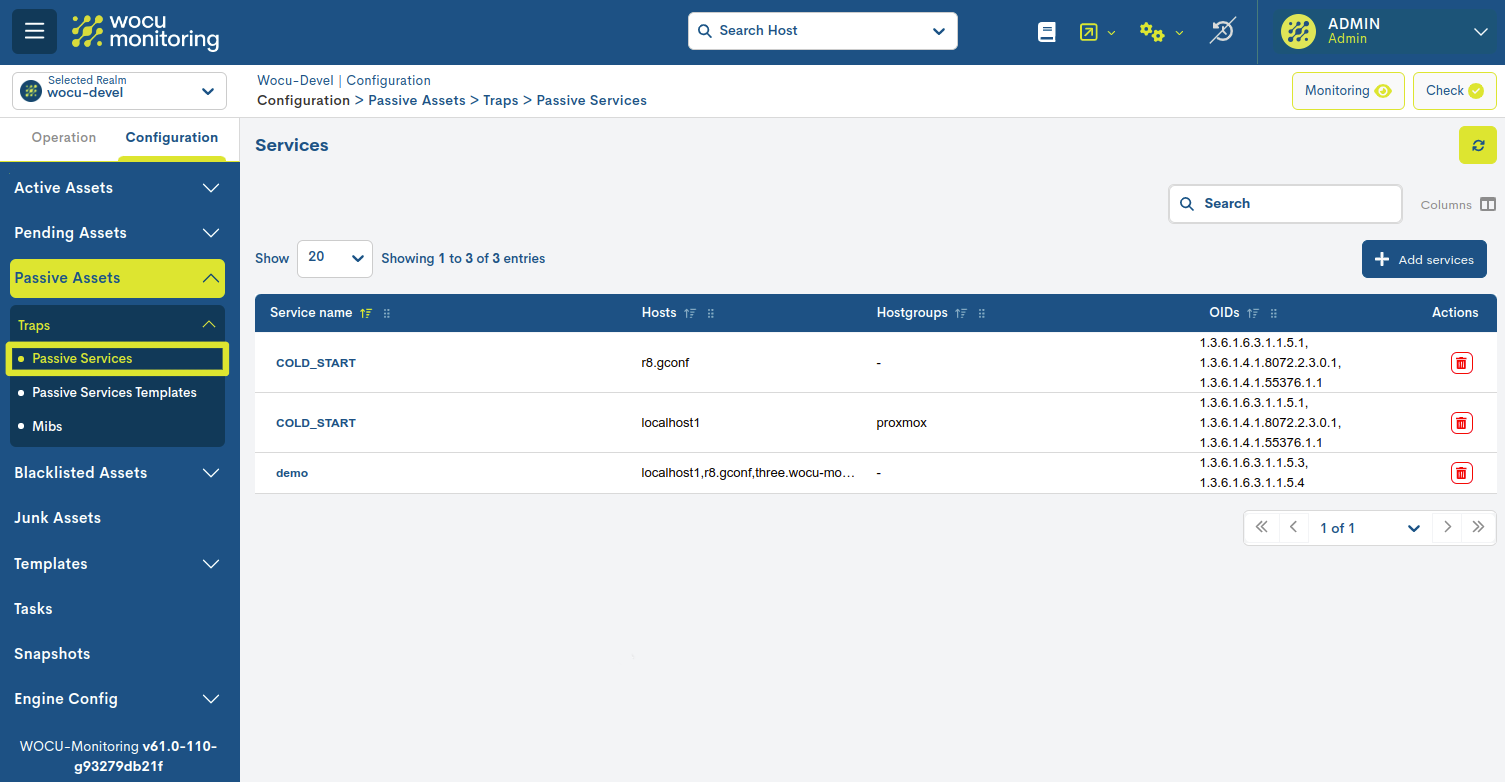
Passive Services list fields
The different fields/columns of the table are described below:

- ✓ Service name
Template of the Passive Service linked to the Host. This element must be previously configured in Passive Services Templates.
- ✓ Host
Linked device.
- ✓ Hostgroups
Linked Host Group(s).
- ✓ OIDs
Unique identifier of SNMP Traps.
Actions
The possible actions applicable to each entry in the table are described below:
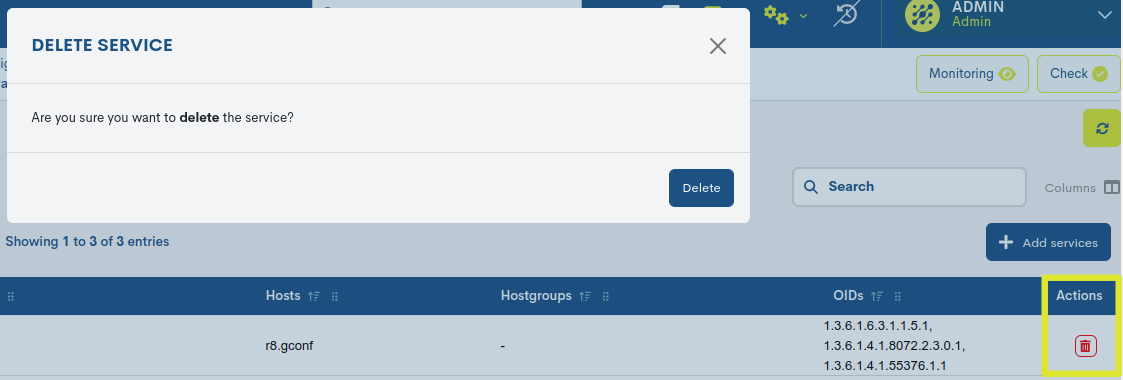
- ✓ Delete: Proceeds to the final deletion of the operation.
The monitoring relationship established between the Host and the Passive Service.
To consolidate the deregistration, it will be necessary to confirm the action in the following dialogue box:
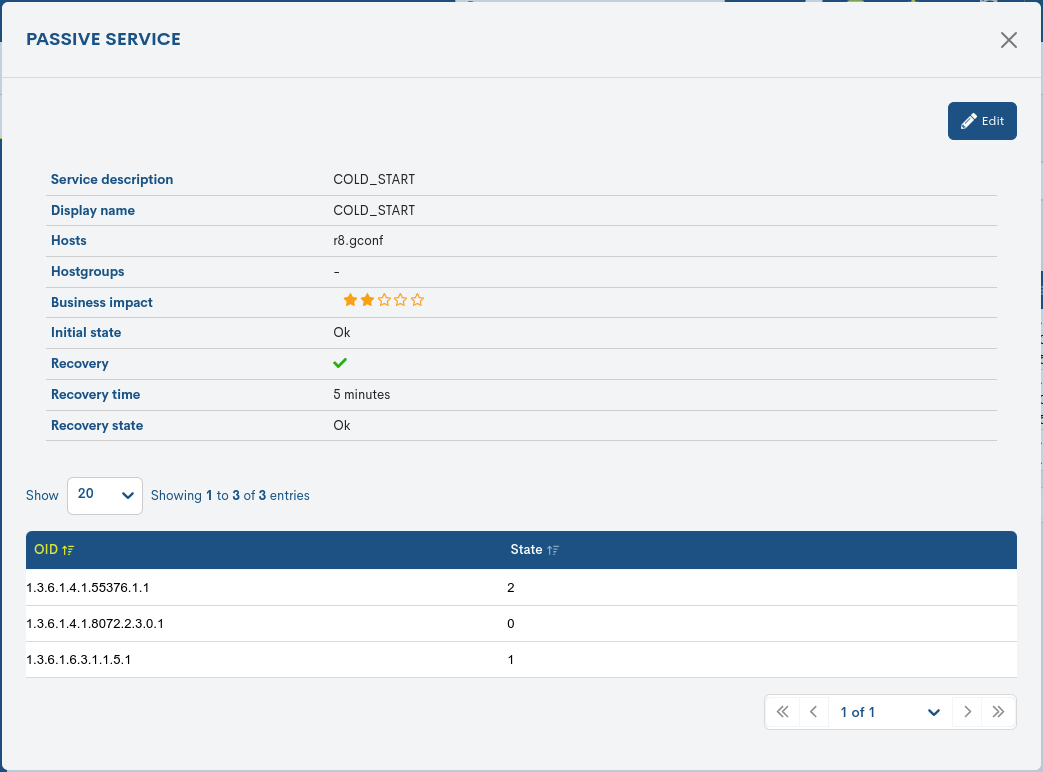
Detailed information on the Service
By clicking on the name of a specific item, the corresponding detail view will pop up with the configuration values of the different attributes of the service registered in the system.
The user is referred to section Add new Services, where these configuration attributes are described in detail.
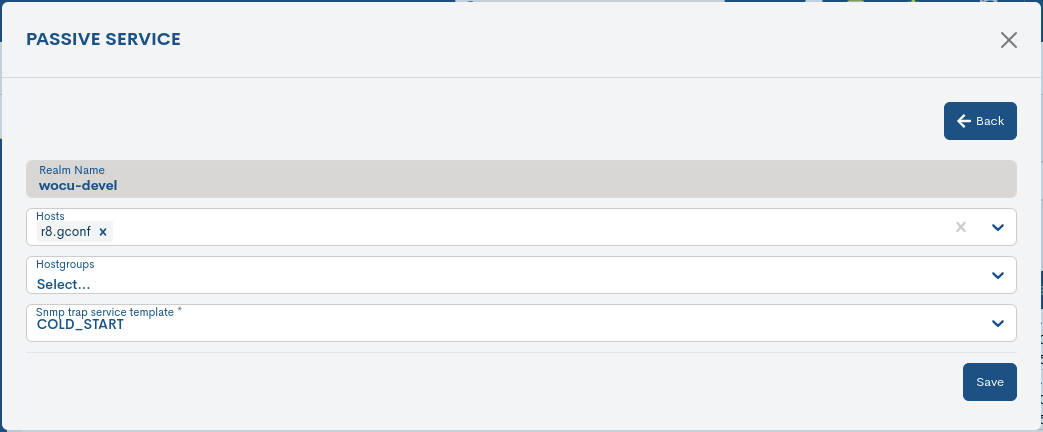
The system also allows changes to the service configuration to be made from the information modal itself. The Edit button provides access to the editable form with the original service configuration parameters, for free modification and updating.
Add new Services
The addition of a new relational model shall be initiated from the + Add Services button.
This process is described below, together with the corresponding fields and parameters to be configured in the following form:
✓ Realm name: field indicating the name of the Realm where the new Passive Monitoring Service will run.
✓ Host: selector of one or more Hosts that will register and implement the new Passive Monitoring Service.
✓ Hostgroups: selector of one or more Host Groups that will register and implement the new Passive Monitoring Service.
✓ Snmp trap service template: Passive Services template selector that will be linked to the previous selected items in order to monitor them. This element must be previously configured in Passive Services Templates.
Once the desired configuration is obtained, it is necessary to save and consolidate the changes made by clicking on the Create button.
Finally, any configuration done in this module requires the execution of the action Check to become effective.
Passive Services Templates
Second instance of the Passive Monitoring alternative method configuration ecosystem.
From this location the user can design and model new Passive Services from templates, for next binding to Hosts and initiate passive communication and receive transcendental situations.
Note
A Template on its own has no value in the system, it must be linked to a Host in order to originate a functionally operational Passive Service.
Therefore, the Passive Services Templates table hosts the passive monitoring models to later associate to Hosts. This correlation is established from section Passive Services.
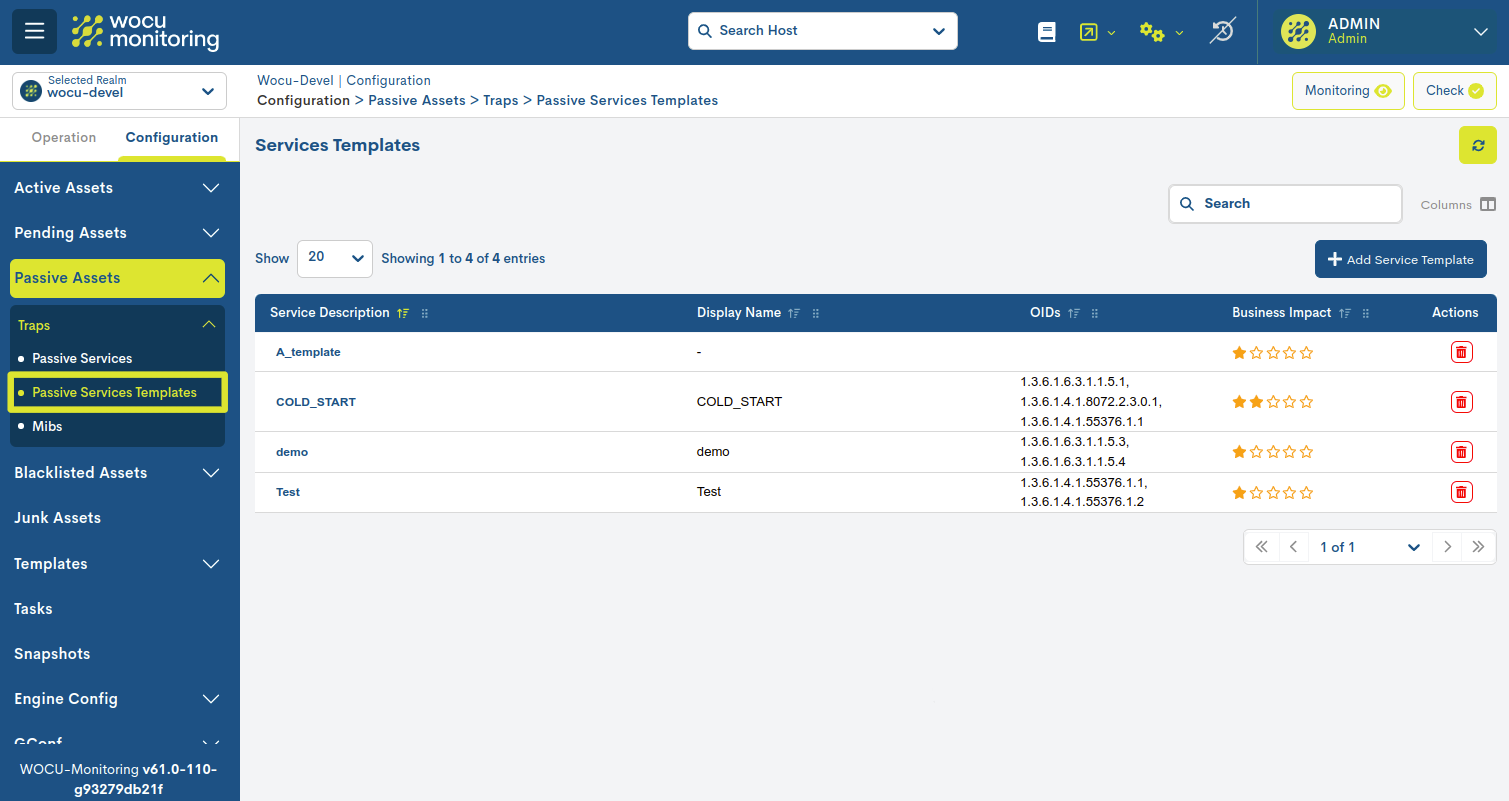
Passive Services Templates list fields
The different fields/columns of the table are described below:

✓ Service Description: descriptive name of the template that models a Passive Monitoring Service.
✓ Display Name: name assigned to the template to be displayed on the screen. It can be used to identify the element with its alias or an easy-to-remember nickname.
✓ Business Impact: this field marks a value on a six-grade scale (from 0 to 5) indicating the importance or significance of the element defined in WOCU-Monitoring. The values are:
None: 0 stars
Low : 1 star
Medium: 2 stars
High: 3 stars
Very High: 4 stars
Review: 5 stars
Actions
The possible actions applicable to each entry in the table are described below:
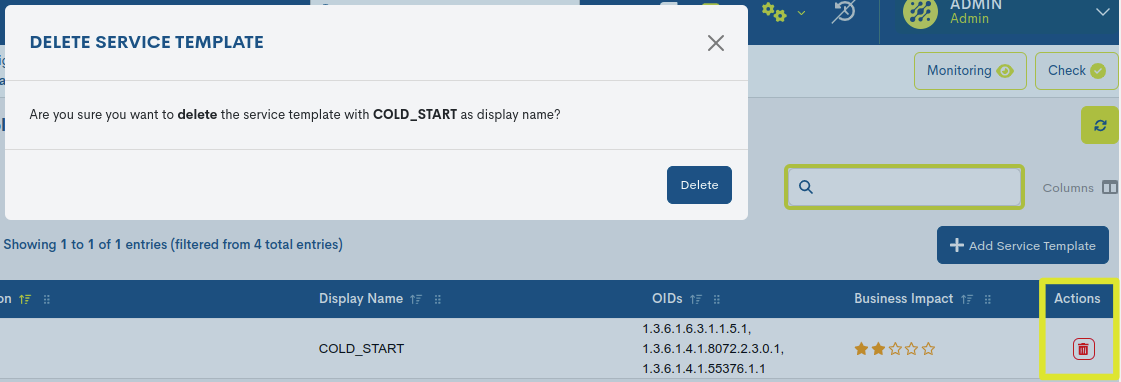
✓ Delete: proceeds to the definitive deletion of a specific template.
To consolidate the deregistration, it will be necessary to confirm the action in the following dialogue box:
Detailed Template Information
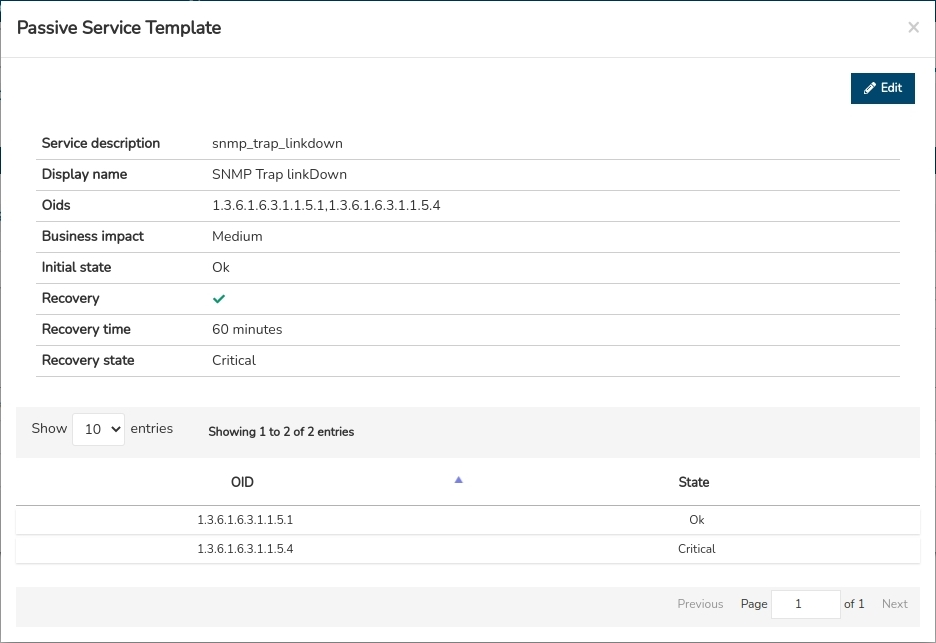
By clicking on the name of a specific item, the corresponding detail view will pop up with the configuration values of the different attributes of the template registered in the system.
The user is referred to section Add Services Template, where these configuration attributes are described in detail.
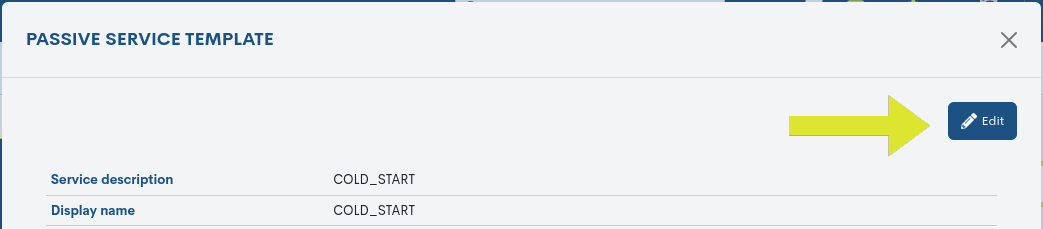
The system also allows changes to be made to the template configuration from the information modal itself. Through the Edit button, you can access the editable form with the configuration parameters of the original template, for free modification and updating.
Add Services Template
The system offers the possibility for the user to manually enter new Passive Services Templates. As many templates as desired can be added.
The registration of a new model will be initiated from the button + Add Service Template. This process is described below along with the corresponding fields and parameters to be configured in the following form:
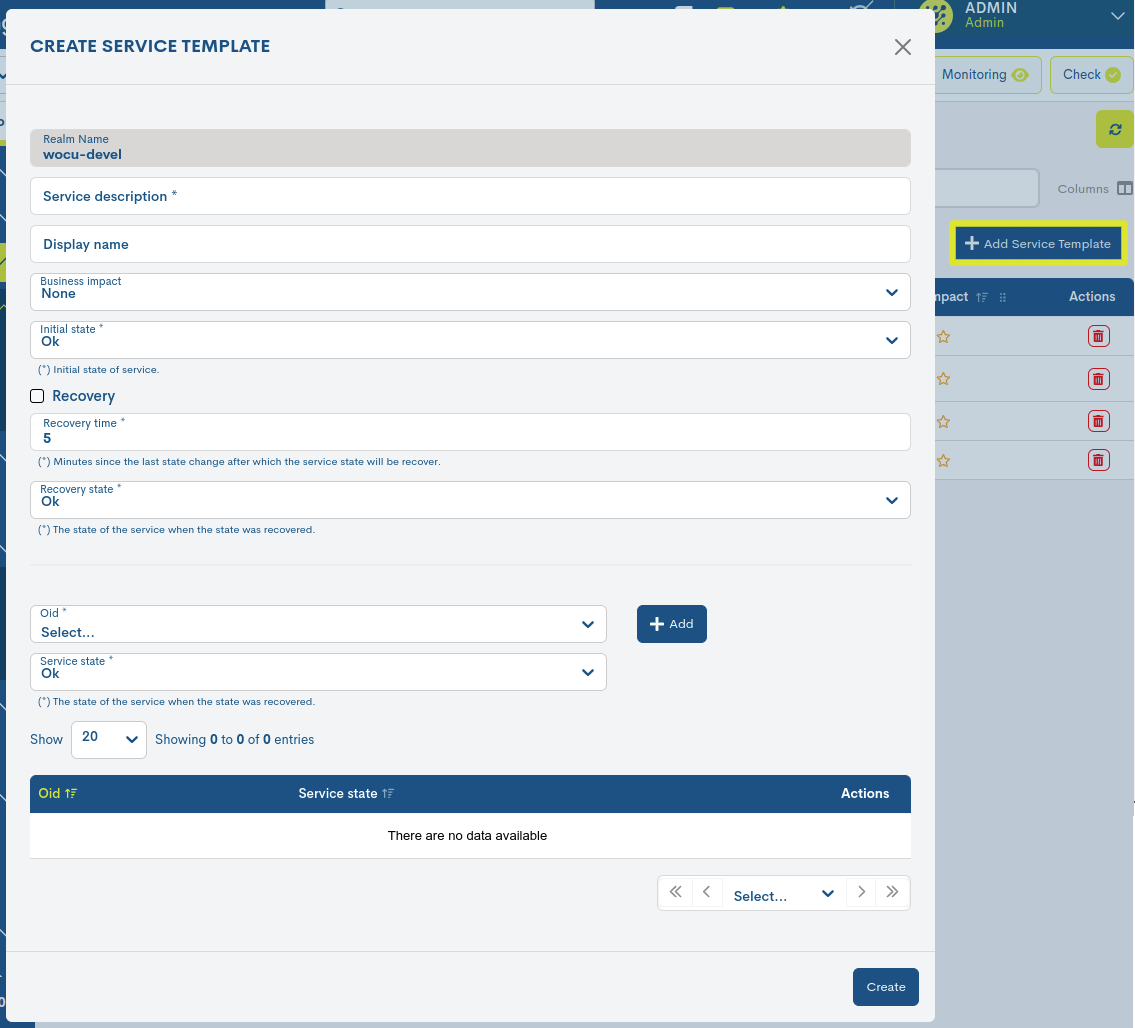
✓ Realm name: field indicating the name of the Realm where the new Passive Monitoring Service will run.
✓ Service Description: descriptive name of the template that models a Passive Monitoring Service.
✓ Display Name: name assigned to the template to be displayed on the screen. It can be used to identify the element with its alias or an easy-to-remember nickname.
Business Impact: this field specifies a value on a six-grade scale (from 0 to 5) indicating the importance or significance of the element defined in WOCU-Monitoring. The values are:
None: 0 stars
Low : 1 star
Medium: 2 stars
High: 3 stars
Very High: 4 stars
Review: 5 stars
Initial state: drop-down to select the initial or starting Statements of Assets in WOCU of this passive service. The options are:
Critical
Warning
Unknow
OK
✓ Revocery: by enabling this option, when the Service exceeds the time threshold defined in the Recovery Time field, the status shall automatically change to the one configured in the Recovery State attribute.
✓ Revocery Time: seconds from the last state change after which the state selected in the Recovery State attribute shall be recovered.
✓ Revocery State: selector of the operational state to which the service shall change to after exceeding the time threshold defined in the Recovery Time attribute.
Important
Attributes of type Recovery are useful for handling unimportant events that cause recurring warnings in the system, generating (sometimes) noise.
Remember that unlike active monitoring, this method does not process notifications for status changes after a check.
✓ OID: selector of an OID (Unique Identifier of SNMP Trap with a monitoring function) previously imported from the MIBS section.
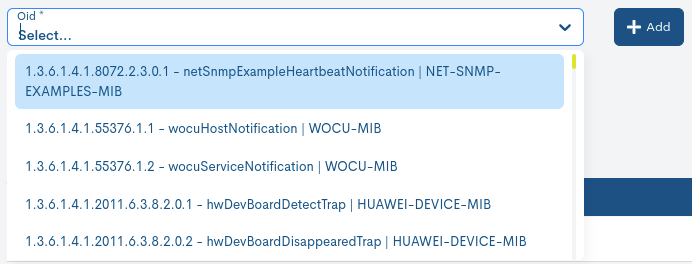
✓ Service State: selector of the state that the Service will assume when it receives a SNMP Trap with the OID selected above.
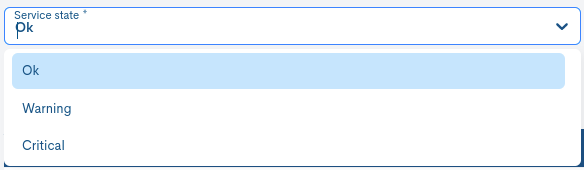
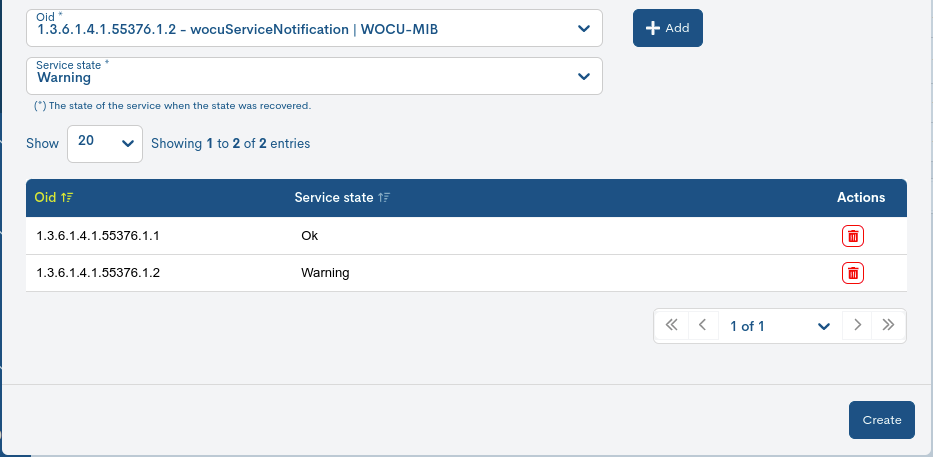
It will be necessary to add these configuration criteria using the + Add button, in order to consolidate them. A new entry is then registered for each OID defined.
Finally, save your changes by clicking on the Create button. This new template will now be available in the Passive Services Templates table.
Note
A Template on its own has no value in the system, it must be linked to a Host in order to originate a functionally operational Passive Service.
MIBS
Third instance of the Passive Monitoring alternative method configuration ecosystem.
In Grosso mode, in monitoring via SNMP Traps, passive communication is established in which WOCU-Monitoring acts as the receiving system. Each SNMP Trap is identified by an OID (unique identifier composed of whole numbers separated by dots). The format in which the message travels is not readable by the receiver. At this point, the information file called MIBS (Managed Information Base) comes into play, which helps to interpret SNMP Traps.
Therefore, the first step to configure and initiate a passive communication channel is to import a MIB containing an OID identifier. In this position, the user will be able to configure a Service that monitors SNMP Traps with that OID and provide the logic that the system requires to subsequently generate events on particular situations.
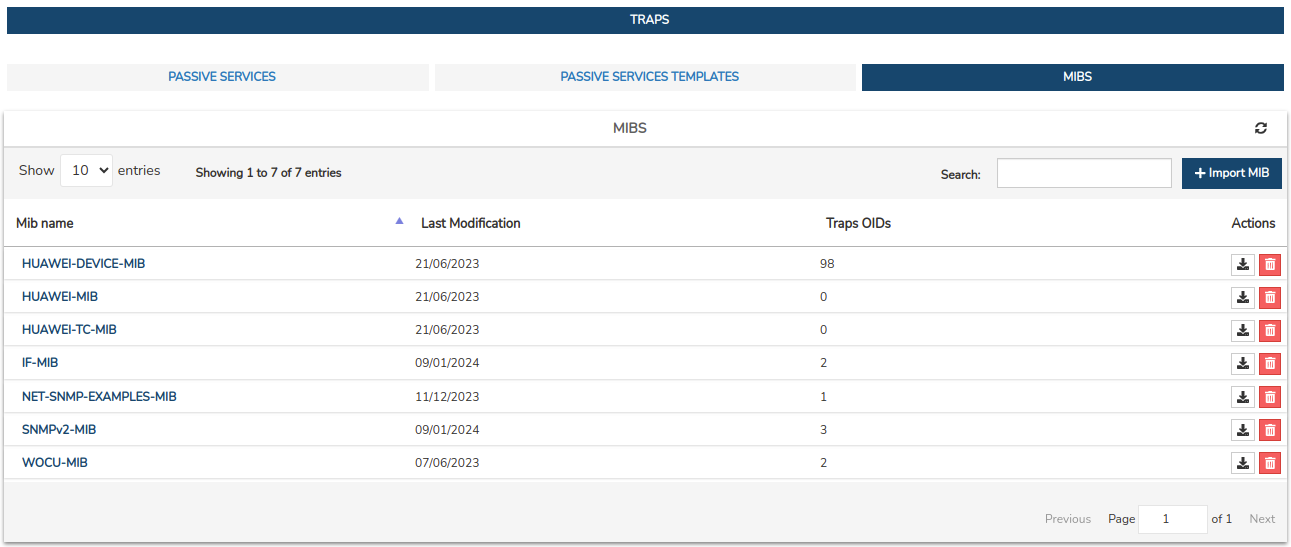
MIBS listing fields
The different fields/columns of the table are described below:
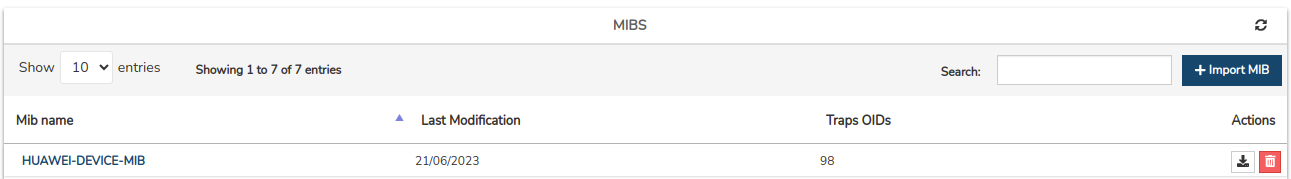
✓ MIB Name: Identifying name of the file within the system.
✓ Last Modification: the exact date on which the last update of the file was recorded.
✓ Traps OIDs: indica el número de OIDs de tipo Trap/Notification que contiene la MIB en cuestión.
Actions
The possible actions applicable to each entry in the table are described below:
✓ Download: facilitates the download of the file. Executing this action will start downloading the file to the hard disk for further processing or use.
✓ Delete: proceeds to the definitive deletion of a specific file. To consolidate the deletion, it will be necessary to confirm the action in the following dialogue box.
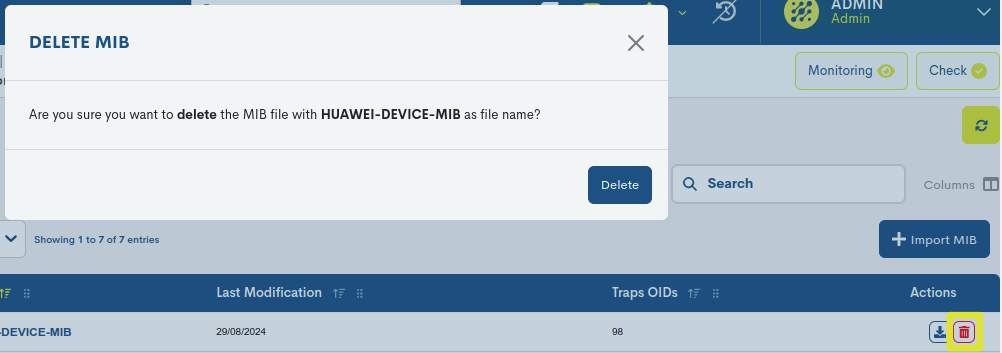
Detailed information on the MIB
Clicking on the name of a specific item will bring up its corresponding detail view with the different OIDs linked to the imported file.
Note
The user is referred to section Add Services Template, where these configuration attributes are described in detail.
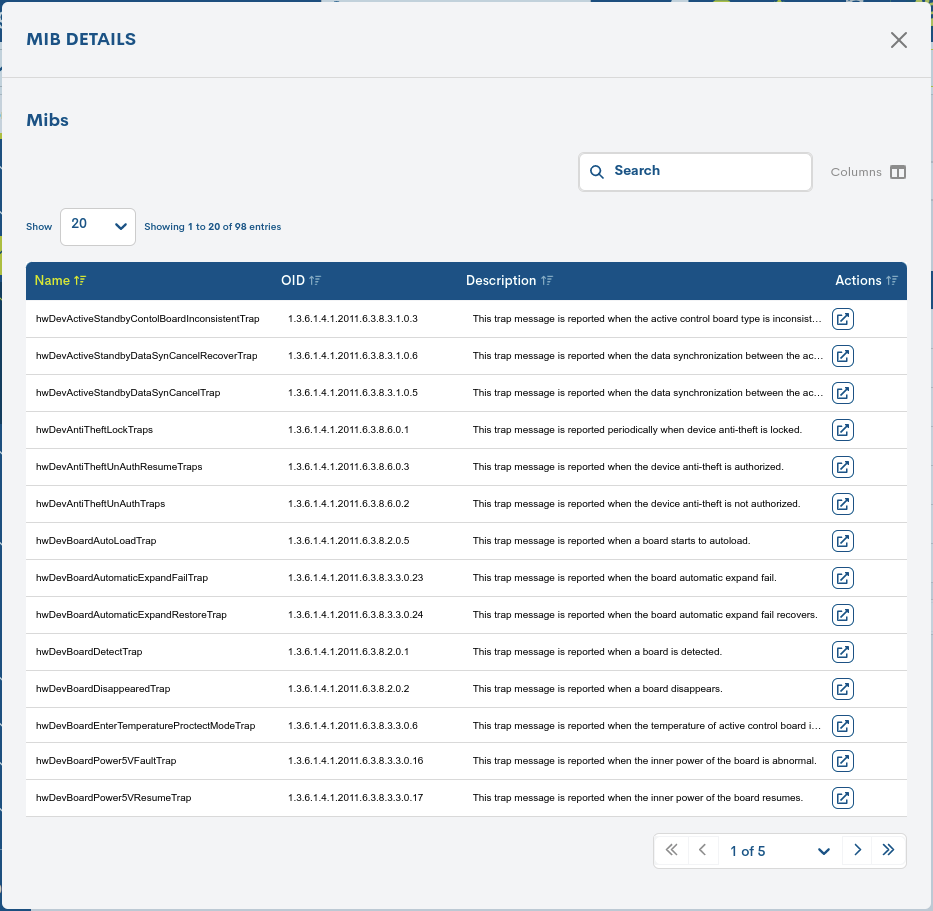
The different fields/columns of the table are described below:
✓ Name: Identifying name of the file within the system.
✓ OID: unique identifier of SNMP Traps.
✓ Description: additional information related to the OID.
✓ Actions: from this position it is possible to Add Services Template from the OID corresponding to the positioned entry.
Import of MIB files (+ Import MIB)
The first step to configure and start a passive communication channel is the import of a MIB containing an OID identifier.
To do this, click on the blue + Import MIB button at the top right of the list.
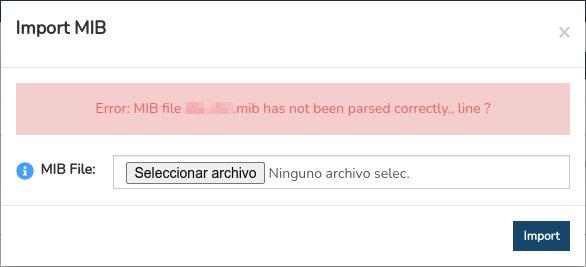
The following import window will then appear:
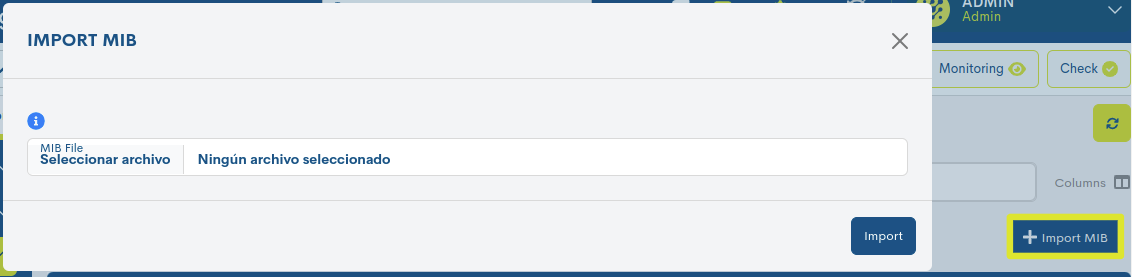
The import process is very simple, you only have to attach the file of the MIB to import, in the MIB file field. Finally, it is necessary to confirm the action to load the file in the global panel. The new MIB will then be available for use if required.
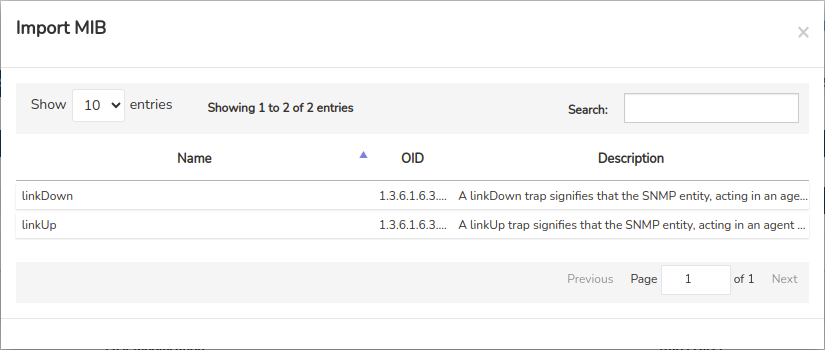
The new MIB is presented with its respective data in the following window, indicating that it is already available for use if required.
When an error occurs while attempting an import, the system will return the following error message, providing information about what happened. The import cannot be carried out until the situation is resolved.